Godot Version
4.3.stable.official [77dcf97d8]
Question
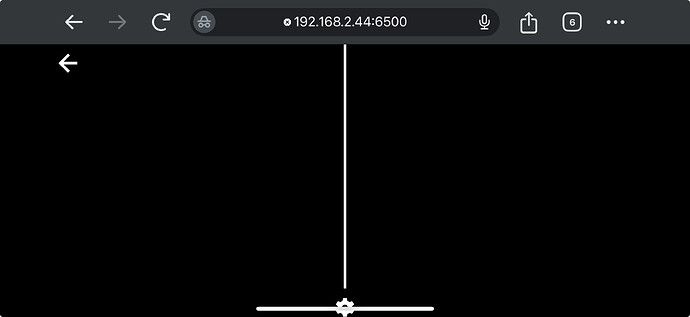
When I try to view the exported web files from my iOS device’s browser - Safari/Chrome, I see a black screen. When i view the same export through my quest browser it works as expected.
What I see in my iOS Device Browser:
I am serving it through node’s http-server.
I’ve been playing around with aframe before finding out about Godot so I am fairly new. I want to get into WebXR development but been stuck on this for quite some time so any help would be appreciated! ![]()
Project is setup using Compatibility
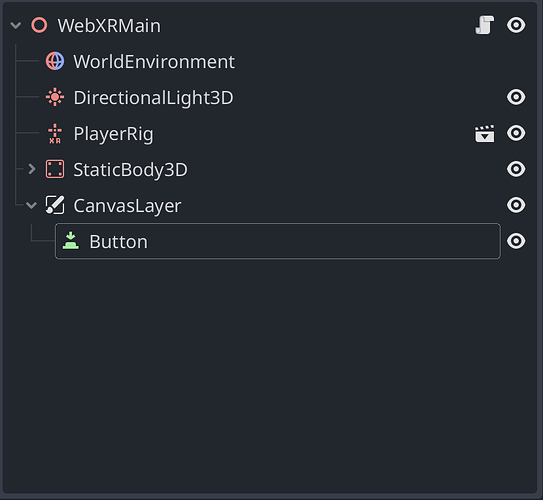
Scene Tree:
Attached Script to WebXRMain:
extends Node3D
var webxr_interface
var vr_supported = false
func _ready():
$CanvasLayer.visible = false
$CanvasLayer/Button.pressed.connect(self._on_button_pressed)
webxr_interface = XRServer.find_interface("WebXR")
if webxr_interface:
# WebXR uses a lot of asynchronous callbacks, so we connect to various
# signals in order to receive them.
webxr_interface.session_supported.connect(self._webxr_session_supported)
webxr_interface.session_started.connect(self._webxr_session_started)
webxr_interface.session_ended.connect(self._webxr_session_ended)
webxr_interface.session_failed.connect(self._webxr_session_failed)
# This returns immediately - our _webxr_session_supported() method
# (which we connected to the "session_supported" signal above) will
# be called sometime later to let us know if it's supported or not.
webxr_interface.is_session_supported("immersive-vr")
func _webxr_session_supported(session_mode, supported):
if session_mode == 'immersive-vr':
if supported:
$CanvasLayer.visible = true
else:
OS.alert("Your browser doesn't support VR")
func _on_button_pressed():
# We want an immersive VR session, as opposed to AR ('immersive-ar') or a
# simple 3DoF viewer ('viewer').
webxr_interface.session_mode = 'immersive-vr'
# 'bounded-floor' is room scale, 'local-floor' is a standing or sitting
# experience (it puts you 1.6m above the ground if you have 3DoF headset),
# whereas as 'local' puts you down at the XROrigin.
# This list means it'll first try to request 'bounded-floor', then
# fallback on 'local-floor' and ultimately 'local', if nothing else is
# supported.
webxr_interface.requested_reference_space_types = 'bounded-floor, local-floor, local'
# In order to use 'local-floor' or 'bounded-floor' we must also
# mark the features as required or optional. By including 'hand-tracking'
# as an optional feature, it will be enabled if supported.
webxr_interface.required_features = 'local-floor'
webxr_interface.optional_features = 'bounded-floor, hand-tracking'
# This will return false if we're unable to even request the session,
# however, it can still fail asynchronously later in the process, so we
# only know if it's really succeeded or failed when our
# _webxr_session_started() or _webxr_session_failed() methods are called.
if not webxr_interface.initialize():
OS.alert("Failed to initialize")
return
func _webxr_session_started():
$CanvasLayer.visible = false
# This tells Godot to start rendering to the headset.
get_viewport().use_xr = true
# This will be the reference space type you ultimately got, out of the
# types that you requested above. This is useful if you want the game to
# work a little differently in 'bounded-floor' versus 'local-floor'.
print("Reference space type: ", webxr_interface.reference_space_type)
# This will be the list of features that were successfully enabled
# (except on browsers that don't support this property).
print("Enabled features: ", webxr_interface.enabled_features)
func _webxr_session_ended():
$Button.visible = true
# If the user exits immersive mode, then we tell Godot to render to the web
# page again.
get_viewport().use_xr = false
func _webxr_session_failed(message):
OS.alert("Failed to initialize: " + message)
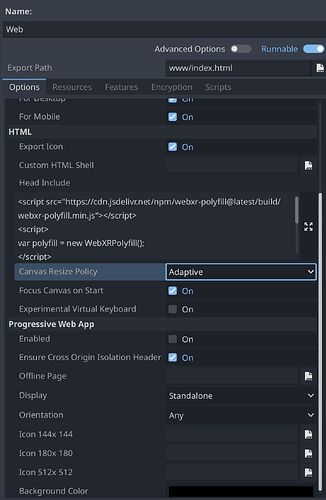
Web Export Config: