Godot Version
v4.4.1.stable.official
Question
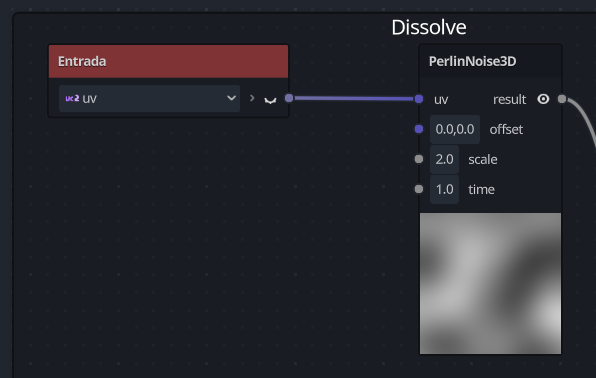
I was trying to use the noise visual shader custom node of this tutorial but the offset variable is missing when the code compiles.
The error message
Just in case the first line means (Expression expected, found: ‘PERIOD’) but I think it is just because the name of the variable is missing, and it finds the next comma.
ERROR: :110 - Expresión esperada, encontrada: 'PERIOD'.
ERROR: Shader compilation failed.
vec3(n_out22p0, 0.0) / / n_in20p2 / n_out23p0
--Main Shader--
1 | shader_type canvas_item;
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | vec3 mod289_3(vec3 x) {
8 | return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0;
9 | }
10 |
11 | vec4 mod289_4(vec4 x) {
12 | return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0;
13 | }
14 |
15 | vec4 permute(vec4 x) {
16 | return mod289_4(((x * 34.0) + 1.0) * x);
17 | }
18 |
19 | vec4 taylorInvSqrt(vec4 r) {
20 | return 1.79284291400159 - 0.85373472095314 * r;
21 | }
22 |
23 | vec3 fade(vec3 t) {
24 | return t * t * t * (t * (t * 6.0 - 15.0) + 10.0);
25 | }
26 |
27 |
28 | float cnoise(vec3 P) {
29 | vec3 Pi0 = floor(P);
30 | vec3 Pi1 = Pi0 + vec3(1.0);
31 | Pi0 = mod289_3(Pi0);
32 | Pi1 = mod289_3(Pi1);
33 | vec3 Pf0 = fract(P);
34 | vec3 Pf1 = Pf0 - vec3(1.0);
35 | vec4 ix = vec4(Pi0.x, Pi1.x, Pi0.x, Pi1.x);
36 | vec4 iy = vec4(Pi0.yy, Pi1.yy);
37 | vec4 iz0 = vec4(Pi0.z);
38 | vec4 iz1 = vec4(Pi1.z);
39 |
40 | vec4 ixy = permute(permute(ix) + iy);
41 | vec4 ixy0 = permute(ixy + iz0);
42 | vec4 ixy1 = permute(ixy + iz1);
43 |
44 | vec4 gx0 = ixy0 * (1.0 / 7.0);
45 | vec4 gy0 = fract(floor(gx0) * (1.0 / 7.0)) - 0.5;
46 | gx0 = fract(gx0);
47 | vec4 gz0 = vec4(0.5) - abs(gx0) - abs(gy0);
48 | vec4 sz0 = step(gz0, vec4(0.0));
49 | gx0 -= sz0 * (step(0.0, gx0) - 0.5);
50 | gy0 -= sz0 * (step(0.0, gy0) - 0.5);
51 |
52 | vec4 gx1 = ixy1 * (1.0 / 7.0);
53 | vec4 gy1 = fract(floor(gx1) * (1.0 / 7.0)) - 0.5;
54 | gx1 = fract(gx1);
55 | vec4 gz1 = vec4(0.5) - abs(gx1) - abs(gy1);
56 | vec4 sz1 = step(gz1, vec4(0.0));
57 | gx1 -= sz1 * (step(0.0, gx1) - 0.5);
58 | gy1 -= sz1 * (step(0.0, gy1) - 0.5);
59 |
60 | vec3 g000 = vec3(gx0.x, gy0.x, gz0.x);
61 | vec3 g100 = vec3(gx0.y, gy0.y, gz0.y);
62 | vec3 g010 = vec3(gx0.z, gy0.z, gz0.z);
63 | vec3 g110 = vec3(gx0.w, gy0.w, gz0.w);
64 | vec3 g001 = vec3(gx1.x, gy1.x, gz1.x);
65 | vec3 g101 = vec3(gx1.y, gy1.y, gz1.y);
66 | vec3 g011 = vec3(gx1.z, gy1.z, gz1.z);
67 | vec3 g111 = vec3(gx1.w, gy1.w, gz1.w);
68 |
69 | vec4 norm0 = taylorInvSqrt(vec4(dot(g000, g000), dot(g010, g010), dot(g100, g100), dot(g110, g110)));
70 | g000 *= norm0.x;
71 | g010 *= norm0.y;
72 | g100 *= norm0.z;
73 | g110 *= norm0.w;
74 | vec4 norm1 = taylorInvSqrt(vec4(dot(g001, g001), dot(g011, g011), dot(g101, g101), dot(g111, g111)));
75 | g001 *= norm1.x;
76 | g011 *= norm1.y;
77 | g101 *= norm1.z;
78 | g111 *= norm1.w;
79 |
80 | float n000 = dot(g000, Pf0);
81 | float n100 = dot(g100, vec3(Pf1.x, Pf0.yz));
82 | float n010 = dot(g010, vec3(Pf0.x, Pf1.y, Pf0.z));
83 | float n110 = dot(g110, vec3(Pf1.xy, Pf0.z));
84 | float n001 = dot(g001, vec3(Pf0.xy, Pf1.z));
85 | float n101 = dot(g101, vec3(Pf1.x, Pf0.y, Pf1.z));
86 | float n011 = dot(g011, vec3(Pf0.x, Pf1.yz));
87 | float n111 = dot(g111, Pf1);
88 |
89 | vec3 fade_xyz = fade(Pf0);
90 | vec4 n_z = mix(vec4(n000, n100, n010, n110), vec4(n001, n101, n011, n111), fade_xyz.z);
91 | vec2 n_yz = mix(n_z.xy, n_z.zw, fade_xyz.y);
92 | float n_xyz = mix(n_yz.x, n_yz.y, fade_xyz.x);
93 | return 2.2 * n_xyz;
94 | }
95 |
96 |
97 | void fragment() {
98 |
99 | vec2 n_out22p0 = UV;
100 |
101 |
102 |
103 | float n_out23p0 = 1.000000;
104 |
105 |
106 | float n_out20p0;
107 |
108 | float n_in20p2 = 2.00000;
109 | {
E 110-> n_out20p0 = cnoise(vec3((vec3(n_out22p0, 0.0).xy + .xy) * n_in20p2, n_out23p0)) * 0.5 + 0.5;
111 | }
112 |
113 |
114 | COLOR.rgb = vec3(n_out20p0);
115 | }
116 |
Poor fix
I could solve this issue temporarily assigning the uv variable in the second slot instead of the offset by changing the second input var from 1 to 0.
func _get_code(input_vars, output_vars, mode, type):
return output_vars[0] + " = cnoise(vec3((%s.xy + %s.xy) * %s, %s)) * 0.5 + 0.5;" % [input_vars[0], input_vars[0], input_vars[2], input_vars[3]]
I copy pasted the code of the tutorial just in case I missed out something, and it gives the same error, so I would like to know why is this happening.
Thanks in advance : )